|
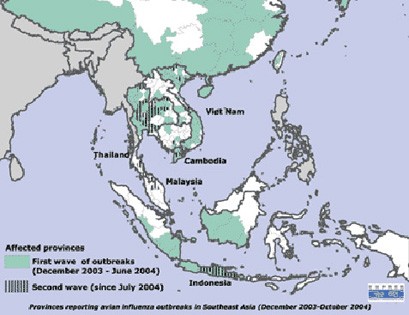
Geographical distribution of AI virus types of Avian Influenza isolated in Asia
|
|
|
|
Newly affected provinces
Outbreaks of AI reported between December 2003 and October 2004
|
|
|
Cross Cutting Issues
- Epidemic is evolving, persisting and expanding in geographical distribution and incidence
- Disease control measures not fully applied in all countries due to structural, financial, political problems
- Biosecurity Measures needed to be applied
- Intensify public awareness to change attitudes and practices of farmers especially on biosecurity
- Culling with insufficient protection of workers and in-humane killing of birds
- Vaccination
- Need for adequate epidemiological assessment
- More studies on asymptomatic animals
- Continuing threat to human health as long as the infection is present in the poultry production systems in Asia
Issues Concerned from the Second Wave
- Disease observed more in less bio-secure system: small-medium
- Disease occurred in (/close to) the area with history of previous outbreak: insufficient culling or movement control or less cooperation
- Collecting points of eggs/poultry
- Live bird markets
- Role of ducks in transmission of disease
|
3. Response of FAO
- FAO is implementing 17 HPAI-related projects at a total value of US$6.2m.
- National projects for infected countries
- Regional networking projects to improve diagnosis, reporting, prevention and control of HPAI
+ projects are in place for Southeast Asia and East Asia and a similar project is planned
for South Asia.
- FAO is collaborating closely with OIE
+ formulation of Guiding Principles & Recommendations on surveillance, prevention,
control and eradication of HPAI
+ identification and conduct of research programmes, technical support and training
activities.
- FAO has established the EMPRES Emergency Centre for Transboundary Animal Disease
Operations (ECTAD)
+ to facilitate coordination and to strengthen the chain of command for FAO
programmes and projects relevant to HPAI and other transboundary animal diseases.
|
4. Recommended National Actions
Recommended National Actions as can be learned from the Conclusions from workshops in Cambodia, Indonesia, Lao PDR, Thailand and Vietnam
|
|
Subject
|
Points mentioned in conclusions
|
|
A.I.
|
Will take time to eradicate
|
|
Priority areas
|
High human density areas close to cities as that is where outbreaks tend to occur
|
|
Market
|
Breaking the chain of transmission by weekly holiday/cleaning day
|
|
Credit
|
Farmers want subsidised credit ? to be weighed against timeliness and sustainability
|
|
The outreach question
|
Roles of government and private sector
|
|
Government
|
Private sector
|
|
Commercial companies
|
Producer orgs. and community groups
|
NGOs
|
| Vet and tech services |
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
Surveillans
Epidemiology and Laboratory Capacity |
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
|
Communication and public awareness reduce impact
example from 2 communes in Vietnam (Source: VSF)
|
Commune
|
1
|
2
|
| First outbreak |
Late December, 2003
|
February 5, 2004
|
| Information to farmers and Animal Health Workers |
Not informed
|
Informed
|
| Time to stamping out |
More than 2 months ? in a 3 km radius
|
Less than 1 week in a 500 m radius
|
| Poultry officially dead |
14,366
|
2,838
|
|
|
Subject
|
Points mentioned in conclusions
|
| Human resource development |
Need at all levels and not only in technical disciplines: border check posts |
|
|
|
Public awareness
|
|
Border control
|
May reduce demand for illegally moved animals |
|
Transparency
|
Could lead to quicker action |
|
Coordination
|
Awareness and transparency may lead to faster coordination and action |
|
To the previous page |